En
Superior Protection
Built-in circuitry safeguards against radio frequency interference, electromagnetic interference, and lightning surges.
Optimal Cold Weather Operation
Features automatic heating in freezing conditions thanks to its sensitive temperature sensor.
Robust and Durable Construction
Utilizes a secure maze connection for the wind cup and housing, high-grade bearings, a corrosion-resistant stainless steel wind cup, and a durable aluminum alloy housing with polyester coating.
Excellent Environmental Resistance
The internal PCB is protected against water, salt fog, and sand-dust through conformal coating and glue sealing.
Flexible Integration
Offers various signal output options for different systems.

AIT- FA21 Wind Combined Sensor | |
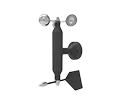 | |
Conforms to Certification | IEC61326 |
Electrical Parameters | |
Operating Voltage | 12VDC~30VDC |
Operating Current | 100mA Max |
Heating Voltage | 18VDC~30VDC |
Heating Power | ≤100W |
Heating Principle | PTC Auto-heating |
Principle of Measurement | Non-contact Magnetic Encoder Scanning |
Entry cable | Aviation connector |
Cable Slip Line Configuration | 6-core Shielded Wire With Aviation Plug: 6*0.5mm²+1*0.5mm² |
Mechanical | |
Colour | Cationic Oxidized Black |
Main Material | 6061/Anodizing |
Anemometer Cup Material | 5052/Anodizing |
Weathervane Material | Carbon Fibre +SS304 |
Bearing Material | Corrosion-resistant SS440C |
Parameter Weight | 1.1kg |
Operating Temperature | -40℃~+70℃ |
Operating Humidity | IEC60068-2-3 0~100%RH |
Vibration Resistance Level | 5-10Hz,d=3mm 10-500Hz,a=2g |
Ingress Protection (IP) rating | IEC60529,IP65 |
Smoke Level | ISO9227 720h |
Meteorological | |
Starting Threshold | ≤0.5m/s Vu=20 C |
Anti-wind Level | >70m/s |
Range of Wind Direction Measurement | 0°~360° |
Wind Direction Measurement Accuracy | ±2° |
Wind Direction Resolution | 0.35° |
Wind Speed Measurement Range | 0 m/s ~50 m/s |
Wind Speed Resolution | 0.1 m/s |
Wind Speed Measurement Accuracy | ±0.5m/s or ±3%V MAX |
A wind direction sensor, commonly referred to as a wind vane, operates by aligning itself with the direction of airflow and converting this orientation into an electrical signal. The front of the wind direction sensor is designed with an aerodynamic fin that naturally rotates until it faces the incoming wind, stabilizing along the true wind direction. High-precision position detection elements—such as magnetic encoders, potentiometers, or Hall-effect sensors—then measure the vane’s angular position and output corresponding directional data in degrees.
In more advanced ultrasonic wind direction sensor models, paired transducers evaluate differences in sound wave travel time across multiple axes to determine wind direction without moving parts. These sensors offer high reliability, fast response, and minimal maintenance.
